ADS hydraulics
ADS is short for Adaptive Damping System (german Adaptiv Dämpfung System). It is hydraulic operated and electronically controlled system. It covers two functions. Constant vehicle level regardless of load and variable electronic control of suspension damping.
System consists from following main components.
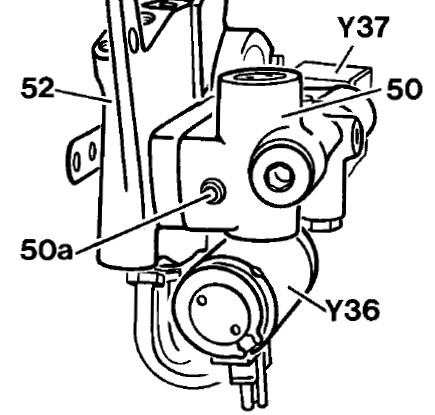
Dampers
Dampers are shock absorbers that are divided into 3 components.
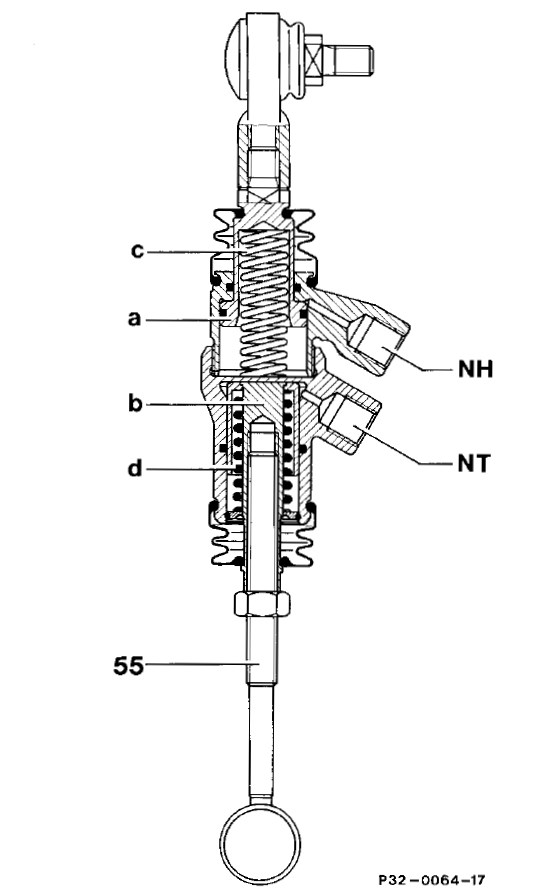
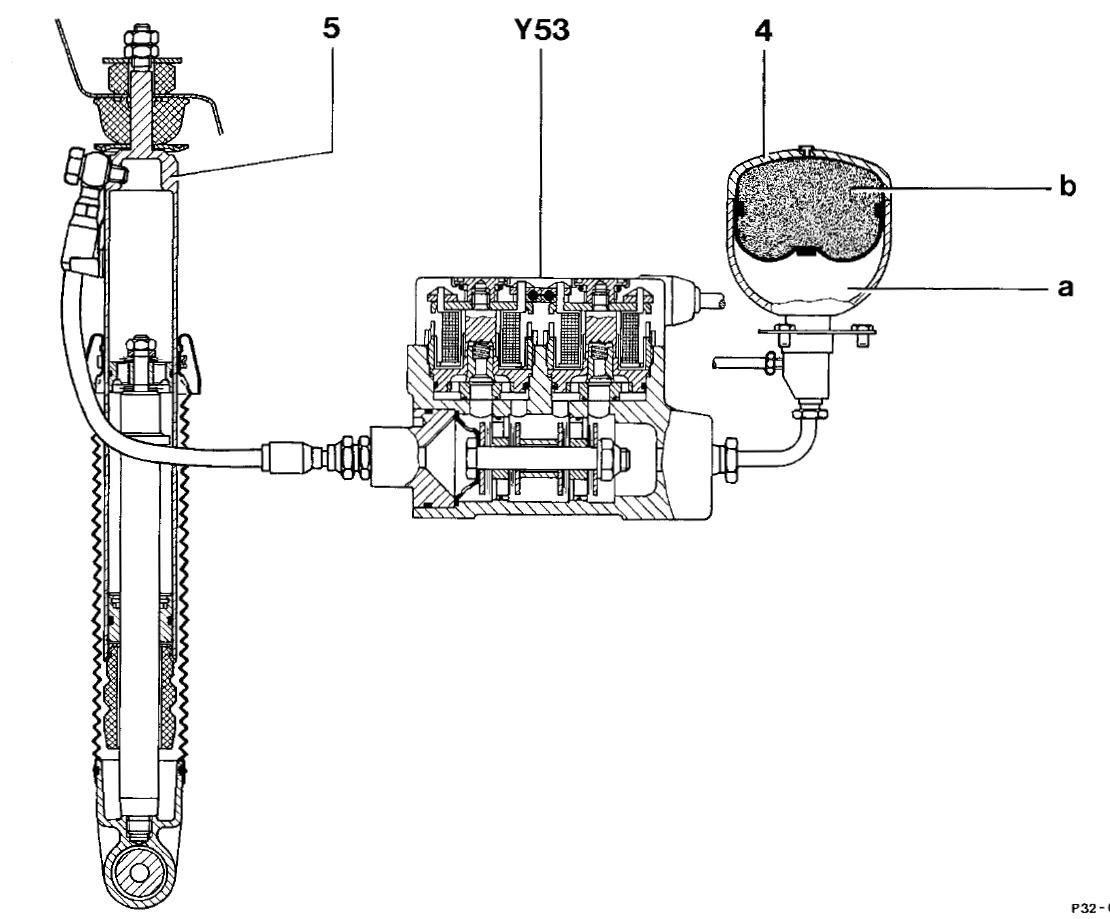
1. Strut (5)- by function it is hydraulic cylinder. When tire hits bump cylinder rod is pushed in cylinder barrel and oil is pushed out of strut. When tire falls in pothole cylinder rod is pulled out of cylinder barrel and oil is sucked to strut. Additionally by filling the cylinder with pressurized oil cylinder extracts. This is then leveling vehicle up.
2. Damper valve (Y53) - This part is responsible for choking the oil passage during tire vertical movement (cylinder retraction and extraction). By normal shock absorbers it is inside of it. The external damper valve allows changing its characteristics - rate of oil flow by electric operated valves. Nowadays it can be integrated within strut itself.
3. Pressure reservoir (4)- This part is hollow vessel filled with pressurized gas (b) separated from oil (a) by diaphragm. This ensures space for oil pushed from strut and its prompt return back to strut.